All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
This five-year general rule and two adhering to exemptions apply just when the proprietor's death sets off the payment. Annuitant-driven payments are discussed below. The initial exemption to the basic five-year rule for individual beneficiaries is to accept the survivor benefit over a longer duration, not to surpass the anticipated life time of the beneficiary.
If the beneficiary chooses to take the survivor benefit in this method, the advantages are strained like any type of various other annuity repayments: partially as tax-free return of principal and partly gross income. The exclusion proportion is discovered by utilizing the deceased contractholder's expense basis and the anticipated payouts based on the beneficiary's life span (of much shorter duration, if that is what the beneficiary chooses).
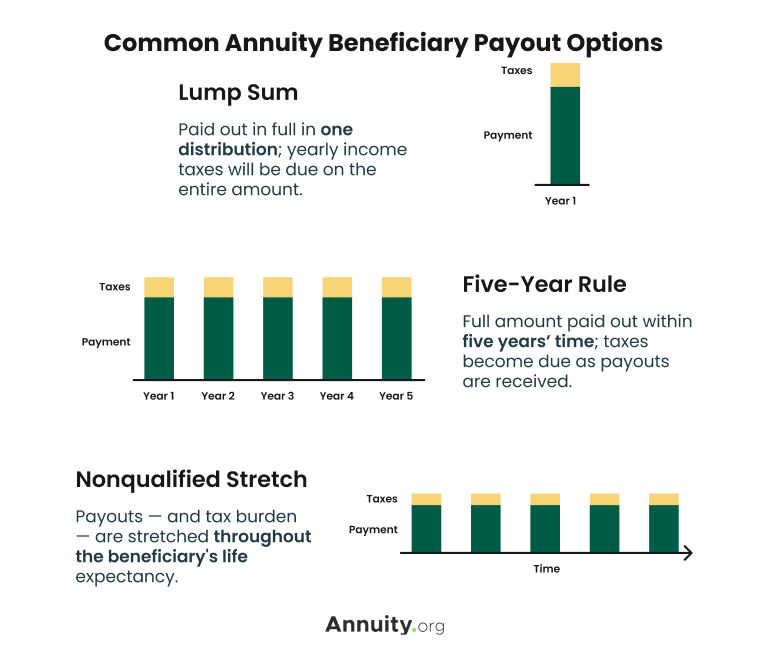
In this approach, in some cases called a "stretch annuity", the recipient takes a withdrawal annually-- the needed quantity of yearly's withdrawal is based upon the exact same tables used to compute the called for distributions from an IRA. There are two benefits to this technique. One, the account is not annuitized so the recipient keeps control over the cash value in the contract.
The second exception to the five-year rule is offered only to a making it through partner. If the marked beneficiary is the contractholder's partner, the spouse might choose to "tip into the shoes" of the decedent. Basically, the partner is treated as if he or she were the proprietor of the annuity from its beginning.
Inherited Annuity Death Benefits taxation rules
Please note this applies only if the partner is called as a "assigned beneficiary"; it is not available, for example, if a depend on is the beneficiary and the partner is the trustee. The general five-year guideline and the two exemptions just put on owner-driven annuities, not annuitant-driven agreements. Annuitant-driven contracts will certainly pay survivor benefit when the annuitant dies.

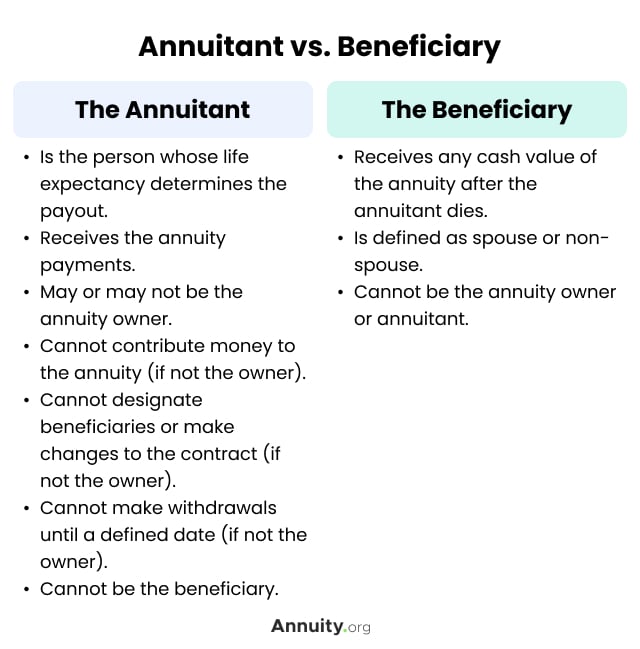
For objectives of this conversation, assume that the annuitant and the proprietor are various - Guaranteed annuities. If the agreement is annuitant-driven and the annuitant dies, the fatality causes the survivor benefit and the recipient has 60 days to choose exactly how to take the survivor benefit based on the regards to the annuity contract
Note that the alternative of a partner to "tip into the shoes" of the owner will not be readily available-- that exemption uses just when the owner has actually died yet the proprietor didn't die in the circumstances, the annuitant did. Last but not least, if the beneficiary is under age 59, the "fatality" exception to prevent the 10% charge will certainly not put on a premature distribution again, because that is offered just on the death of the contractholder (not the death of the annuitant).
Many annuity business have interior underwriting plans that reject to provide contracts that call a different owner and annuitant. (There might be odd situations in which an annuitant-driven agreement meets a clients special needs, yet usually the tax obligation downsides will outweigh the benefits - Guaranteed annuities.) Jointly-owned annuities may position comparable troubles-- or at the very least they may not serve the estate planning function that various other jointly-held properties do
Consequently, the death advantages must be paid out within five years of the very first proprietor's fatality, or based on the 2 exemptions (annuitization or spousal continuance). If an annuity is held jointly in between a couple it would appear that if one were to die, the various other might merely proceed ownership under the spousal continuation exception.
Think that the other half and better half named their son as recipient of their jointly-owned annuity. Upon the fatality of either owner, the company has to pay the fatality benefits to the boy, that is the beneficiary, not the surviving spouse and this would most likely beat the owner's purposes. Was hoping there may be a system like establishing up a beneficiary IRA, yet looks like they is not the case when the estate is arrangement as a beneficiary.
That does not recognize the kind of account holding the inherited annuity. If the annuity was in an acquired individual retirement account annuity, you as executor ought to have the ability to designate the acquired IRA annuities out of the estate to inherited Individual retirement accounts for every estate beneficiary. This transfer is not a taxed event.
Any kind of circulations made from acquired IRAs after project are taxable to the beneficiary that received them at their regular earnings tax obligation rate for the year of distributions. However if the inherited annuities were not in an individual retirement account at her death, after that there is no means to do a direct rollover into an inherited IRA for either the estate or the estate recipients.
If that takes place, you can still pass the circulation via the estate to the individual estate beneficiaries. The income tax obligation return for the estate (Kind 1041) could consist of Kind K-1, passing the income from the estate to the estate recipients to be tired at their individual tax obligation rates rather than the much higher estate revenue tax obligation prices.
Taxes on inherited Annuity Death Benefits payouts

: We will develop a strategy that consists of the finest items and features, such as improved fatality advantages, premium rewards, and long-term life insurance.: Get a tailored method designed to optimize your estate's worth and decrease tax liabilities.: Execute the chosen approach and receive continuous support.: We will aid you with setting up the annuities and life insurance policy policies, providing constant support to make certain the plan continues to be effective.
Needs to the inheritance be regarded as an earnings associated to a decedent, after that tax obligations may apply. Typically talking, no. With exception to pension (such as a 401(k), 403(b), or individual retirement account), life insurance policy profits, and savings bond passion, the beneficiary normally will not need to bear any type of earnings tax obligation on their inherited wealth.
The quantity one can acquire from a depend on without paying taxes relies on various variables. The government inheritance tax exception (Deferred annuities) in the USA is $13.61 million for people and $27.2 million for married pairs in 2024. Individual states may have their very own estate tax regulations. It is advisable to talk to a tax obligation professional for accurate info on this issue.
His mission is to streamline retired life planning and insurance policy, ensuring that customers recognize their selections and protect the most effective insurance coverage at unbeatable prices. Shawn is the owner of The Annuity Professional, an independent on-line insurance policy company servicing customers across the United States. Through this system, he and his group aim to remove the uncertainty in retired life preparation by aiding individuals locate the most effective insurance protection at the most affordable rates.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Highlighting Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Indexed Annuity Key Insights on Immediate Fixed Annuity Vs Variable Annuity Breaking Down the Basics of Pros And Cons Of Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity Pros
Analyzing Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros Cons Everything You Need to Know About Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros Cons Defining Pros And Cons Of Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity Advantages and Disadvan
Exploring the Basics of Retirement Options A Closer Look at Pros And Cons Of Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity Defining the Right Financial Strategy Features of Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Why Fixed An
More
Latest Posts